Usage
Starting Glaciation
Python’s interactive shell is the easiet way to check if Glaciation was correcty installed.
- On Windows, please open a command prompt (
cmd.exe):: $ pip show glaciation $ python Python 3.11.2 (tags/v3.11.2:878ead1, Feb 7 2023, 16:24:28) [MSC v.1934 32 bit (Intel)] on win32 >>>
Import glaciation:
$ import glaciation
>>>
Check version:
$ glaciation.__version__
'1.0.0'
>>>

Executing your first script
Each Glaciation test using the CDU submodule it is made up by 3 files:
variables.json: It contains information about remote CDU connections and variables.
settings.py: Global variables for the test.
test.py: The logic of the test.
variables.json
This json configuration file, contains all the information about remote CDU connections and the variables which are going to be used in the test:
VARDB_NAME: vardb name given to the CDU connection. Maximum 8 characters.
CONNSTRING: CDU connection string.
- DLL:
PERIOD: CDU syncronization period in ms.
- CONTAINER:
VARIABLES: Variables to be used in the test. Maximum of 1024 variables for each vardb.
- MONIT: Field to create a CompactReg/csv monitorization file.
FILE_NAME: File path to be created.
PERIOD: Embedded monit period in ms.
TYPE: Options {1,2,3}. COMPACT_REG(1), TIMON CSV(2), NEW CSV(3).
{
"vardbs": {
"CCU_A": {
"VARDB_NAME": "CCU_A",
"CONNSTRING": "CONNTYPE=ETH; HOST=172.16.3.3; TCPPORT=10000; PWD=password2",
"DLL": "CduAPI.dll",
"PERIOD": "32",
"CONTAINER": "monitcontainer",
"VARIABLES": {
"READ": {
"fwk_internal": ["TEMPERATURE"],
"monitcontainer": ["PLC_HMI_AI_R_Value"],
"CduDiagnosis": ["CONF_Max_monitorization_sessions"]
},
"WRITE": {
"monitcontainer": ["PLC_CAB"]
}
},
"MONIT": {
"FILE_NAME" : "CompactReg_HMI",
"PERIOD" : "32",
"TYPE" : "1",
"VARIABLES" : {
"vardb": ["HMI_VAR1","HMI_VAR2","HMI_VAR3","HMI_VAR4"]
}
}
},
"PXI_DO3": {
"VARDB_NAME": "PXI_DO3",
"CONNSTRING": "DEVICENAME=\"Dev4\"",
"DLL": "ConnNiPxi6512.dll",
"CONTAINER": "",
"VARIABLES": {
"READ": [
],
"WRITE": {
"":[
"PORT0_LINE0","PORT0_LINE1","PORT0_LINE2","PORT0_LINE3",
"PORT1_LINE0","PORT1_LINE1","PORT1_LINE2","PORT1_LINE3",
"PORT2_LINE0","PORT2_LINE1","PORT2_LINE2","PORT2_LINE3",
"PORT3_LINE0","PORT3_LINE1","PORT3_LINE2","PORT3_LINE3",
"PORT4_LINE0","PORT4_LINE1","PORT4_LINE2","PORT4_LINE3",
"PORT5_LINE0","PORT5_LINE1","PORT5_LINE2","PORT5_LINE3",
"PORT6_LINE0","PORT6_LINE1","PORT6_LINE2","PORT6_LINE3",
"PORT7_LINE0","PORT7_LINE1","PORT7_LINE2","PORT7_LINE3"
]
}
}
}
}
}
test.py
This Python script contains the main program to be executed. It raises an Exception if the test execution is not succesfull. Glaciation CDU submodule has 2 main classes (CduAPIWrapper and VardbVarWrapper) which are based in a json configuration file. See #variables-json To use Glaciation modules the only thing you need to do is to import them at the start of the test file. The example below is the most common use of a Glaciation test. It imports CduAPIWrapper and VardbVarWrapper classes and the submodule glaciation.testing.generic which contains the most common functions to be used in a generic CDU test. See:
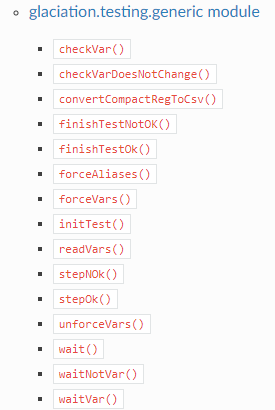
API Reference
The function cdu.runAll() initializes a new process/thread for each vardb defined in the json file. It is possible to start only one of them calling to the function startSync(vardbname). Then the function vdb.loadVars() loads all variables in the vardb and we are ready to start reading and forcing them. If something goes wrong or any of the connexion is missing, the test will Raise an Exception and it will show the error all the way down.
import logging
from settings import *
from glaciation.helper import mainTest
import glaciation.testing.generic as tgf
from glaciation.cdu.api import CduAPIWrapper
from glaciation.cdu.vardb import VardbVarWrapper
@mainTest
def main():
# Start all CDU sync and mon
cdu = CduAPIWrapper(JSON_FILE_NAME)
cdu.runAll(retries=1)
# Connect to all vars using vardbvar
vdb = VardbVarWrapper(JSON_FILE_NAME)
vdb.loadVars()
# read vars
vdb.readVar("CCU_A","fwk_internal::TEMPERATURE")
vdb.readVar("CCU_A","PLC_HMI_AI_R_Value")
vdb.readVar("CCU_A","CduDiagnosis::CONF_Max_monitorization_sessions")
# assert if 3 cdu sessions are available in CCU_P
tgf.checkParam(vdb, "CCU_P","CduDiagnosis::CONF_Max_monitorization_sessions",3)
# wait until temperature is 32 in CCU_A
tgf.waitParam(vdb, "CCU_A", "fwk_internal::TEMPERATURE", 32)
# force var HMI_PLC_CAB in HMI_MON
vdb.forceVar("HMI_MON","HMI_PLC_CAB",1)
# Stop monitorizations and convert CompactReg file to csv
cdu.stopMon()
tgf.convertCompactRegToCsv("CompactReg_HMI", True)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
setting.py
It contains some necessary variables to run the main test.
PROGNAME = "Example" # filled automaticaly if run from rqm
TESTER = "Example Name" # filled automaticaly if run from rqm
LOG_FILE_PATH = "results.txt" # filled automaticaly if run from rqm
DESCRIPTION = "Example test description"
JSON_FILE_NAME= "variables.json"
More examples
You can download some test examples from Scman->Cautto->glaciation or https://gitlab.cafpower.com/glaciation/py-glaciation/examples
Visual Studio Code Setup
Visual studio Code is recommended for development and execution of the tests. Installing the Python (IntelliSense (Pylance)) extension will allow you to run and debug those tests, making your life easier.
Installing an Code Formatter extension is also recommended. This package was written using yapf and black extensions.
After installing Python extension create a launch configuration json and add “cwd”: “${fileDirname}” to it:
installing vscode extension
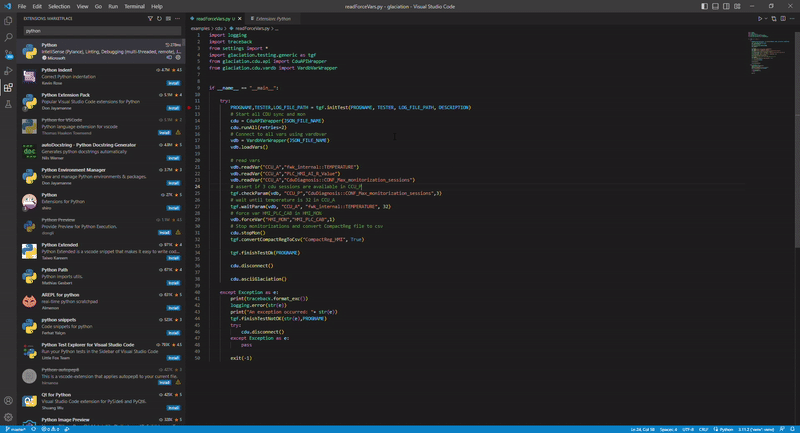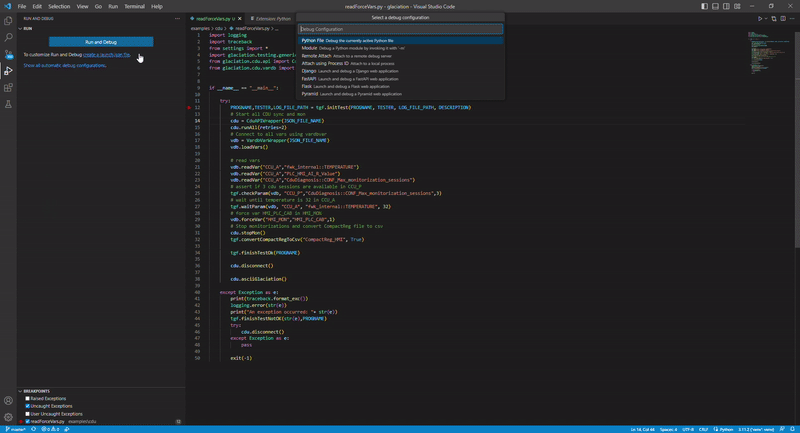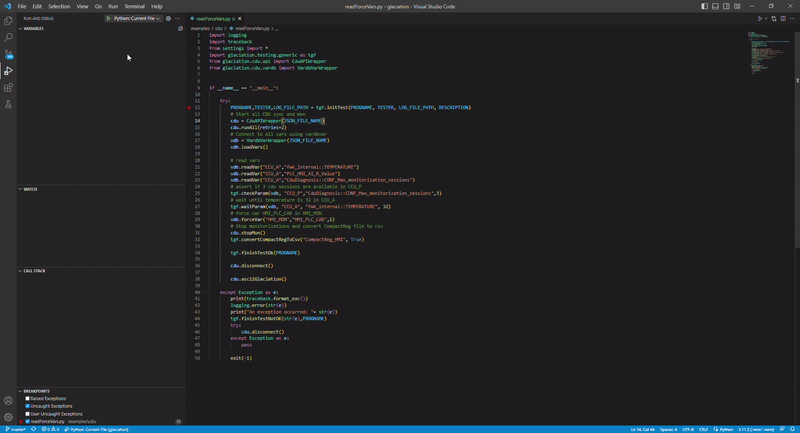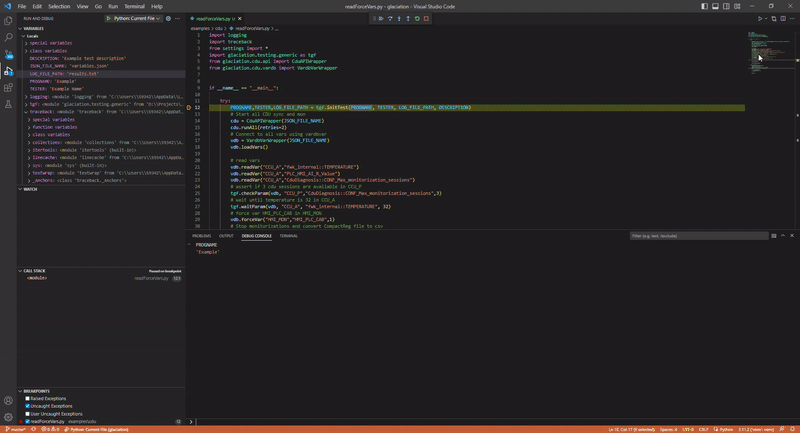
debugging in vscode
{
// Use IntelliSense to learn about possible attributes.
// Hover to view descriptions of existing attributes.
// For more information, visit: https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=830387
"version": "0.2.0",
"configurations": [
{
"name": "Python: Current File",
"type": "python",
"request": "launch",
"program": "${file}",
"console": "integratedTerminal",
"cwd": "${fileDirname}"
}
]
}